Stoloteuthis
Michael Vecchione and Clyde F. E. Roper

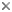
This tree diagram shows the relationships between several groups of organisms.
The root of the current tree connects the organisms featured in this tree to their containing group and the rest of the Tree of Life. The basal branching point in the tree represents the ancestor of the other groups in the tree. This ancestor diversified over time into several descendent subgroups, which are represented as internal nodes and terminal taxa to the right.

You can click on the root to travel down the Tree of Life all the way to the root of all Life, and you can click on the names of descendent subgroups to travel up the Tree of Life all the way to individual species.
For more information on ToL tree formatting, please see Interpreting the Tree or Classification. To learn more about phylogenetic trees, please visit our Phylogenetic Biology pages.
close boxIntroduction
Species of Stoloteuthis are heteroteuthins with arms one forming the primary (subjective category) hectocotylization (unknown in S. weberi) and a tentacular organ but exhibit unusual variability in the dorsal fusion of the head and mantle and the size of the ventral mantle shield. The genus as constituted here probably does not form a natural group due to the inclusion of the poorly known S. weberi and the distinctive Stoloteuthis sp. A. However until both of these two species are better known and we are confident that there are not too many surprises left in the Heteroteuthinae, we prefer not to name a new genus.
Brief diagnosis:
A heteroteuthin with ...
- enlarged suckers on arms II of males (except S. sp. A).
- arms I very broad (hectocotylized) (not apparent in S. weberi).
Characteristics
- Arms
- Arm suckers relatively larger in males but no arm asymmetry present.
- Arms II, in males, with one to several greatly enlarged (encept in S. sp. A).
- Arms I, in males, very broad (not apparent in S. weberi).
- Arm tips in females not modified (except S. sp. A, unknown in S. weberi).
- Suckers of arms IV in females in two identical series (unknown in S. weberi).
 Click on an image to view larger version & data in a new window
Click on an image to view larger version & data in a new window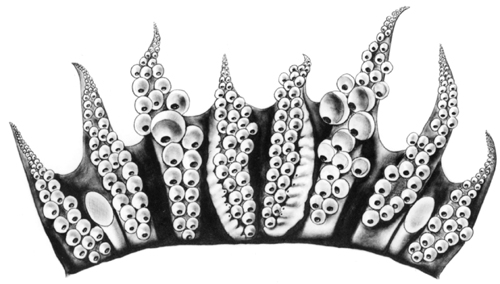
Figure. Oral view of brachial crown (minus tentacles) of S. maoria, mature male, off S.E. New Zealand (44°02'S, 178°08'W), otter trawl at 230-421 m. Drawing by A. Hart.
- Tentacles
- Tentacle organ of club proximal to or barely overlapping sucker-bearing portion of club (unknown in S. weberi).
- Tentacle organ of club proximal to or barely overlapping sucker-bearing portion of club (unknown in S. weberi).
- Funnel
- Funnel/mantle locking-apparatus with straight, simple groove in funnel component or groove with anterior angular pit (unknown in S. weberi).
- Funnel/mantle locking-apparatus with straight, simple groove in funnel component or groove with anterior angular pit (unknown in S. weberi).
- Mantle
- Mantle broadly or narrowly fused to head dorsally, or free.
- Ventral mantle does not extend beyond middle of eyes.
- Fins
- Fin margins rounded posteriorly (except probably in S. maoria).
Comments
S. weberi, which is known only from the type specimen, was formerly placed in Heteroteuthis. This species lacks a dorsal head-mantle fusion, a feature that distinguishes it from all other Stoloteuthis except Stoloteuthis sp. A but in the arrangement of arm suckers, it resembles Stoloteuthis species. S. maoria was formerly placed in Iridoteuthis. Harman and Seki (1990) re-examined S. maoria and found that it was similar to Iridoteuthis iris in its broad head-mantle fusion, middorsal mantle buldge and posteriorly pointed fins. We place S. maoria in Stoloteuthis on the basis of the arm modifications in mature members of both sexes which are similar to S. leucoptera. Most of the generic-level characters, however, are presently unknown in S. weberi. Stoloteuthis sp. A, like S. weberi, was originally placed in Heteroteuthis. However the hectocotylization is very unlike that of Heteroteuthis but resembles that of Stoloteuthis.
Comparison of species
| Dorsal head-mantle fusion | Arm I glands (males) | Arm IV tip suckers | Posterior fin lobe | Shield length as % of VML | |
| S. leucoptera | Narrow | Dorsal & ventral margins | 3-4 series | Rounded | >80 |
| S. maoria | Broad | Ventral margins | 2 series | Sngled (?) | >80 |
| S. weberi | Absent (no fusion) | Unknown | Apparently 2 series | Rounded | Unknown |
| Stoloteuthis sp. A | Absent but fusion of nuchal cartilage. | Uncertain if glands exist | 2 series | Rounded | ~50 |
Life History
Young look similar to adults.Figure. Dorsal and ventral views of young S. leucoptera, 9.8 mm ML. Drawings from Vecchione, et al. (2001).
Distribution
S. leucoptera is known from off the eastern United States and the eastern Atlantic including the Mediterranean Sea; S. weberi from Indonesia (7.6°S, 117.5°E) and S. maoria from off New Zealand. Unidentified species of Stoloteuthis have been reported from near the Kerguelens, Prince Edward Islands (southern Indian Ocean), Discovery Bank (southeast Atlantic (Nesis, 1982/87) and east of Tasmania (Villanueva and Sánchez, 1993).
References
Cairns, S. D. 1976. Biological results of the University of Miami deep-sea expeditions. 118. Cephalopods collected in the Straits of Florida by the R/V Gerda. Bull. Mar. Sci. 26: 233-272.
Nesis, K. N. 1982/87. Abridged key to the cephalopod mollusks of the world's ocean. 385+ii pp. Light and Food Industry Publishing House, Moscow. (In Russian.). Translated into English by B. S. Levitov, ed. by L. A. Burgess (1987), Cephalopods of the world. T. F. H. Publications, Neptune City, NJ, 351pp.
Orsi Relini, L. and D. Massi. 1991. The butterfly squid Stoloteuthis leucoptera in the Mediterranean. J. Mar. Biol. Ass. U. K. 71: 47-51.
Vecchione, M., C. F. E. Roper and M. J. Sweeney. 1989. Marine flora and fauna of the eastern United States. Mollusca: Cephalopoda. NOAA Tech. Rep. NMFS 73: 23 pp.
Vecchione, M., C. F. E. Roper, M. J. Sweeney and C. C. Lu. 2001. Distribution, relative abundance and developmental morphology of paralarval cephalopods in the western North Atlantic Ocean. NOAA Tech Rep. NMFS 152.
About This Page

National Museum of Natural History, Washington, D. C. , USA

Smithsonian Institution, Washington, D. C., USA
Correspondence regarding this page should be directed to Clyde F. E. Roper at
Page copyright © 2015 and
 Page: Tree of Life
Stoloteuthis .
Authored by
Michael Vecchione and Clyde F. E. Roper.
The TEXT of this page is licensed under the
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License - Version 3.0. Note that images and other media
featured on this page are each governed by their own license, and they may or may not be available
for reuse. Click on an image or a media link to access the media data window, which provides the
relevant licensing information. For the general terms and conditions of ToL material reuse and
redistribution, please see the Tree of Life Copyright
Policies.
Page: Tree of Life
Stoloteuthis .
Authored by
Michael Vecchione and Clyde F. E. Roper.
The TEXT of this page is licensed under the
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License - Version 3.0. Note that images and other media
featured on this page are each governed by their own license, and they may or may not be available
for reuse. Click on an image or a media link to access the media data window, which provides the
relevant licensing information. For the general terms and conditions of ToL material reuse and
redistribution, please see the Tree of Life Copyright
Policies.
- Content changed 21 January 2014
Citing this page:
Vecchione, Michael and Clyde F. E. Roper. 2014. Stoloteuthis . Version 21 January 2014 (under construction). http://tolweb.org/Stoloteuthis/20033/2014.01.21 in The Tree of Life Web Project, http://tolweb.org/




 Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site
Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site